
What is Halal? Comprehensive Knowledge for Businesses 2025
Halal today is not only a religious concept but has become a global standard in manufacturing and consumption. Understanding “What is Halal?”, what Halal foods include, and the value Halal certification brings will help businesses seize opportunities in a vast, transparent market with strong growth potential.
1. What is Halal?
Halal is an important concept in Islam, helping Muslim consumers identify what is permissible to use in daily life and activities. Understanding “What is Halal?” not only helps Muslims comply with their religious rules but also serves as a foundation for businesses to develop suitable products and services to approach the broad Halal consumer market.
1.1. Origin and meaning of “Halal” from Arabic and the Qur'an
“Halal” is a term originating from Arabic, mentioned throughout the Qur'an with the meaning “permissible,” “lawful,” or “proper.” In the context of Islam, “permissible” here refers not only to being lawful in daily life but also to conforming to sacred rules set out in Sharia law.
This concept forms a highly strict system of guidelines, helping Muslims distinguish what should be done and what should be avoided in all activities, from eating and consumption to social life. Not only food, but many sectors such as cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, services, finance, and tourism are also applying Halal standards to meet requirements for transparency, safety, and ethics in production and supply processes.
For this reason, Halal is now recognized as a global standard widely acknowledged for its quality and reliability.
1.2. Distinguishing Halal and Haram in Islamic law

In Islamic law, Halal and Haram are two opposite categories used to determine which actions or products are permissible and which are not. Besides these two clear groups, Islamic law also includes the concept of Mashbooh — “doubtful” cases that lack sufficient evidence to determine whether they are Halal or Haram. When encountering products or actions in this grey area, Muslims are generally encouraged to avoid them to ensure the highest level of compliance.
Read more: Halal Standards & International Development Opportunities for Businesses
2. What is Halal food?
Halal food refers to food items prepared according to Islamic religious rules to ensure safety, cleanliness, and the absence of prohibited ingredients. So, what are the common Halal food groups? And what are the principles of Halal food processing?
2.1. Common Halal food groups
In general, many food groups meet Halal criteria as long as their origin and processing comply with Islamic rules. Some common groups include:
- Beef, lamb, goat, deer, venison, chicken, duck, birds… slaughtered according to Islamic rituals, with clear Halal certification.
- Fish, seafood, honey, milk from cows, goats, sheep, camels… without mixing Haram additives.
- Fresh vegetables, frozen vegetables, dried fruits, legumes, and nuts (peanuts, cashews, hazelnuts, chia seeds, walnuts…).
- Grains such as rice, wheat, oats, barley, cereal powders, and grain products that do not use alcohol, gelatin, or additives from non-Halal animals.
In the food industry today, the development of Halal product lines is becoming a trend, as not only Muslims but many other consumers also value these products for their transparency and safety.
2.2. Principles of Halal food processing

For a product to be considered Halal, businesses must strictly follow principles from slaughtering to processing. Some key points include:
- Animals must be alive and healthy at the time of slaughter. The slaughterer must be a Muslim (or Jew) and must recite “Allah” (meaning God) before cutting the throat.
- Slaughtering tools must be sharp, and the cut must be made at the throat to allow maximum blood drainage. The meat is then hung upside down to remove all blood, as blood is non-Halal.
- Animals must be raised on natural feed, without using by-products from Haram animals or prohibited stimulants or hormones.
- Processing, storage, and transportation must be completely separated from Haram foods to avoid cross-contamination (using separate utensils, machinery, kitchen areas, warehouses…).
- This is why businesses need Halal supervision teams at their factories and must operate strict management processes to ensure that all final products meet international Halal standards.
2.3. The role of Halal food in Muslim life
For Muslims, Halal food is not only a dietary choice but also a direct expression of compliance with Sharia law in daily life. Eating Halal helps them maintain their faith and feel assured because each product is verified and supervised according to religious standards. Additionally, the Halal system:
- Creates jobs and career opportunities for Muslims as auditors, supervisors, and Halal supply chain managers.
- Supports the sustainable development of the Halal industry and expands global trade for products meeting Halal standards.
- Enhances food quality and safety, benefiting both Muslim communities and global consumers.
3. What is Halal certification?
To understand Halal more thoroughly—not only as a religious concept but also as a standard in daily life and business—we need to explore how Halal certification is applied to products and services, as well as its meaning for consumers and businesses.
3.1. Definition and purpose of Halal certification
Halal certification is a document issued after evaluating and confirming that a product, service, or production process fully meets Islamic law standards. The certification ensures that the product contains no prohibited (Haram) ingredients and is produced according to Halal principles, from raw materials and processing to storage.
The primary goal of Halal certification is to build trust among Muslim consumers regarding the legality and safety of the product. Additionally, businesses can use the Halal logo as clear evidence of quality and compliance with international standards, thereby enhancing brand credibility and expanding global market access.
Notably, the Halal certification mark not only appears on product packaging but is also used as a communication and branding tool. Businesses can use the Halal logo in:

Some communication activities that can use the Halal mark
- Corporate documents and records: official letters, documents, emails, name cards, company brochures.
- Advertising and marketing: TVCs, radio, newspapers, brochures, marketing materials.
- Transport and outdoor advertising: delivery vehicles, signboards, public posters, accompanied by the name or logo of the certification body.
Thus, Halal certification is not only a religious requirement but also a competitive advantage, contributing to expanding the global Halal ecosystem and creating sustainable business opportunities.
3.2. Common product and service groups requiring Halal certification
Halal is not only a standard for food but also covers many aspects of life and business. Below are typical product and service groups often certified Halal to meet the diverse needs of the market:
- Food and beverages: processed foods, raw materials, and meat products handled according to Halal rituals.
- Cosmetics and personal care products: skincare, haircare, and hygiene products free from prohibited ingredients.
- Pharmaceuticals and supplements: medicines, vitamins, and dietary supplements assessed to meet Halal standards.
- Consumer goods and chemicals: household chemicals such as detergents, laundry powder, and cleaning products.
- Healthcare products: medical tools, bandages, masks, and nutritional products for patients.
- Non-food animal products: materials like leather, wool, furs processed according to Halal standards.
- Restaurant and catering services: restaurants and hotels serving Halal-certified food and services.
- Tourism and travel services: tour operators, hotels, and amenities that comply with Halal requirements.
- Transportation and warehousing services: ensuring no cross-contamination between Halal and non-Halal products.
- Pet-related products and services: pet food and care items free from prohibited ingredients.
4. Scale and key Halal markets
With a population accounting for about 25% of the world, the global Halal market is expanding rapidly. The Halal food sector alone reached USD 2.3 trillion in 2022 and is expected to grow to USD 4.1 trillion by 2030, with an average growth rate of 7.7% per year. These figures show that Halal consumption is increasingly becoming a key standard in global consumer choices.
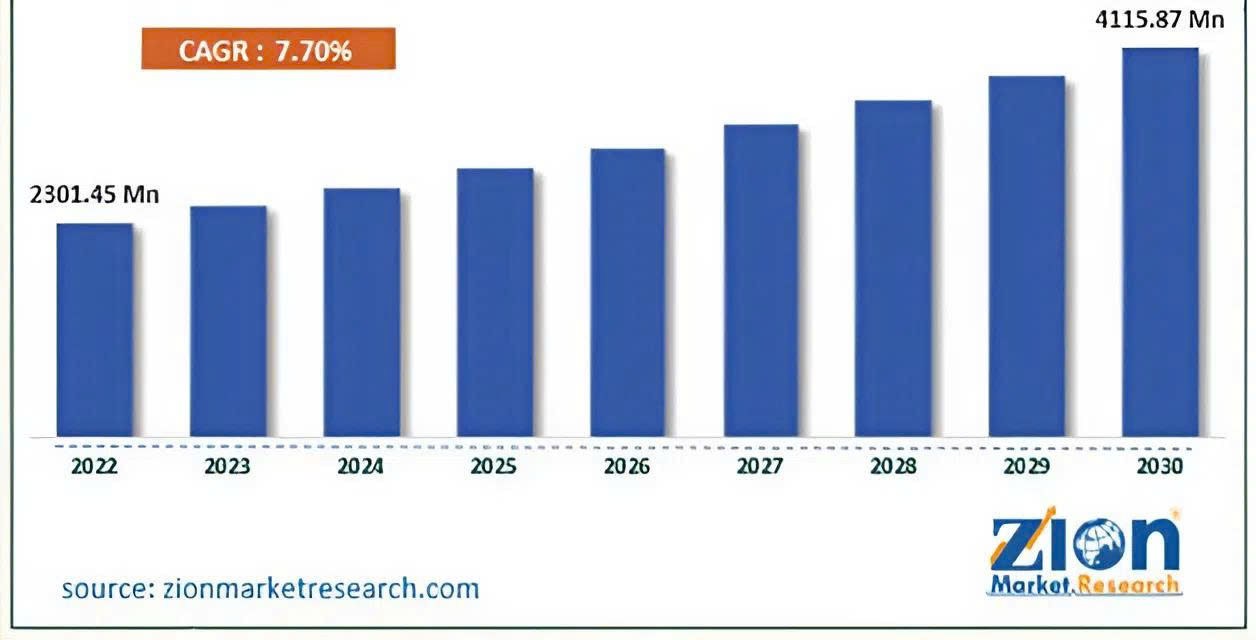
Source: Zion Market Research (India)
Among Halal-consuming regions, Southeast Asia – South Asia – South Pacific is the largest market, serving 860 million Halal food users, accounting for 66% of the global Muslim population. This region has a total consumption value of about USD 470 billion, with Southeast Asia alone contributing USD 230 billion, highlighted by markets such as Malaysia, Indonesia, and Brunei.
Additionally, the Middle East and Africa are emerging markets with high food import demand and stable trade growth. The Gulf countries (UAE, Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait…) with high income levels also prioritize high-quality Halal products.
Overall, the global landscape shows that the Halal market is not only vast but also rich in long-term growth potential. For Vietnam, the Halal market opens enormous export opportunities thanks to its strengths in agriculture, processed foods, and strategic geographic location. By meeting strict certification requirements, Vietnamese businesses can significantly increase export value and expand market share in major markets.
Read more: Top 10 Vietnam’s Key Export Products in 2025
5. Benefits of Halal certification for businesses
Halal certification is not only a “passport” helping businesses enter Muslim markets but also enhances product quality and corporate image.
5.1. Expanding access to Muslim markets
Halal certification helps businesses penetrate countries with high demand for Halal products such as the Middle East, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Muslim communities in Europe and North America. By complying with religious requirements, products are more easily accepted and prioritized, thereby supporting export activities and long-term market growth.
5.2. Enhancing brand credibility and consumer trust
Halal-certified products show that the business maintains strict controls over ingredients and hygiene, building strong consumer trust—not only among Muslims. With transparency and clear quality assurance, brands become more reputable among customers and partners, strengthening competitiveness both domestically and internationally.
6. Conclusion
Halal food is becoming an important part of the global consumer market due to increasing demand from Muslim communities and the trend toward clean, safe products. With impressive growth and expanding scale, this is a major opportunity for businesses to develop suitable products and reach high-potential customers worldwide.
AGlobal – the best cross-border e-commerce solution for businesses.
Register for a free 1-on-1 consultation tailored to your industry right here!
