
Vietnamese Seaweed: Comprehensive Export Guide 2025
The seaweed industry in Vietnam is experiencing strong growth, opening up substantial export potential worldwide. To capture this opportunity, businesses need to clearly understand the requirements for quality standards, export documentation, and international regulations, while also developing suitable market strategies and distribution channels to elevate Vietnamese seaweed products in the global market.
1. Overview of Vietnamese Seaweed and Export Potential
Vietnamese seaweed is considered a highly potential resource, with the marine ecosystem recording more than 800 species, of which about 88 species have economic value and are commercially harvested. In 2023, Vietnam recorded approximately 16,500 hectares of seaweed farming, producing 150,000 tons of fresh seaweed — creating an important foundation for developing a large-scale industry in the future.
To effectively leverage this advantage, the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development (MARD) has set a target of increasing production to 500,000 tons by 2030, while expanding potential farming areas to 900,000 hectares. Once zoning and planning are completed, Vietnam may reach a production capacity of 600,000 – 700,000 tons of dried seaweed annually. This is seen as a major step forward in the industrialization of seaweed farming and processing.
In addition, the global market context is also highly favorable. According to Market Research Future, the global edible seaweed market is growing robustly and is expected to reach a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.87% by 2035. This is an opportunity for Vietnamese seaweed to expand exports, move toward higher-value products, diversify offerings, and develop sustainably.
Read more: Types of Seaweed in Vietnam: Export Potential 2025
2. Outstanding Advantages of Dried Seaweed in Export
Within the seaweed product portfolio, dried seaweed is increasingly showcasing major advantages when exported to international markets. With its distinctive qualities and convenience, dried seaweed enables better adaptation to strict global standards.

4 Key Advantages of Dried Seaweed in Export
2.1. Advantages in Preservation and Transportation
Dried seaweed has low moisture content, significantly reducing microbial growth, mold, and extending shelf life. When properly stored in a dry, cool environment away from direct sunlight, dried seaweed products can maintain quality for 9–15 months, and with optimal methods, up to 2–3 years.
Additionally, dried seaweed is lightweight and compact, making transportation easier and reducing shipping costs — a crucial benefit for long-distance exports.
2.2. Retains Nutritional Value and Product Quality
Studies show that using modern drying techniques such as freeze-drying helps preserve most minerals, vitamins, and bioactive compounds in seaweed. This ensures the product maintains its “superfood” value when it reaches consumers. Furthermore, preserving the natural color and quality enhances user experience and product appeal.
2.3. Increases Product Value and Enables Deep Processing
Dried seaweed opens opportunities for product diversification — from seaweed snacks and low-carb noodles to functional foods. Compared to fresh seaweed, dried varieties allow for more advanced processing, resulting in higher profit margins. Deep processing also creates a full “value chain”: farming, pre-processing, processing, and final products — enabling exports not only of raw materials but of branded, high-value goods.
2.4. Easier Compliance With International Food Safety Standards
With standardized processes from harvesting to drying, packaging, and storage, dried seaweed ensures stricter control of microbiology, moisture, impurities, and heavy metals. This facilitates compliance with international food safety standards.
Additionally, businesses can apply quality management systems and food safety certifications to enhance credibility, making products more trustworthy and ready for entry into high-standard markets.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Exporting Vietnamese Seaweed
To export Vietnamese seaweed successfully, businesses must prepare thoroughly and comply with all necessary procedures. Below are the steps to understand, prepare, and optimize export opportunities in global markets:
3.1. Preparing a Complete Product
To prepare products for export, businesses must first thoroughly research the market to understand consumer needs, as well as the standards and regulations of each country. Based on this information, businesses can develop more suitable products and optimize quality, packaging, and food safety to retain nutritional value and meet the requirements of importing markets.
3.1.1. Ensuring Product Quality
Product quality is the most crucial factor influencing consumer purchasing decisions—especially in demanding markets such as the U.S., EU, or Japan. For food products like seaweed, businesses must strictly control each stage of production to ensure hygiene, maintain flavor, color, and nutritional value.
Doing so not only helps products meet international standards but also enhances credibility and builds trust with customers.
3.1.2. Product Packaging and Labeling

Sample reference for seaweed packaging
To preserve and highlight the product’s value in international markets, packaging plays a highly important role and must ensure:
- Food safety: Packaging must not contain harmful substances and must not affect the product.
- Preservation capability: Maintains quality, flavor, color, and nutritional value during storage and transportation.
- Clear information: Includes product name, ingredients, Nutrition Facts panel, expiry date, and storage instructions.
- Compliance with international standards: Meets requirements such as FDA Labeling (U.S.) or sustainable packaging regulations (EU).
3.2. Completing Mandatory Export Documentation and Certifications
Businesses must prepare all required documents and certifications to ensure smooth customs clearance and compliance with international regulations.
3.2.1. Business Licenses and Legal Registration
Businesses must possess valid business licenses and complete all required legal registrations, including:
- Export-related business registration
- Tax registration
- Business registration with relevant authorities
- Food-related licenses
These procedures establish the legal basis for conducting international trade agreements, ensuring lawful rights for both businesses and partners, while facilitating smooth customs clearance.
3.2.2. Product Certifications and Testing

Some important food safety certifications for export
These certifications not only enable the product to qualify for export but also enhance brand credibility and value in global markets.
Read more: What Is Halal Certification? Regulations for Halal Food
3.2.3. Commercial and Customs Documentation
Commercial and customs documents consist of all paperwork required to declare and transport export goods, including:
- Sales Contract: Defines rights and obligations of buyer and seller
- Commercial Invoice: Details quantities, value, delivery terms, and payment
- Packing List: Specifies number of packages, weight, and volume
- Bill of Lading: Confirms receipt of goods by the carrier and commitment to deliver
- Customs Declaration: Provides details of goods for customs clearance
Preparing accurate and complete documentation ensures smooth export procedures and minimizes delays or risks during international shipping.
3.3. Selecting Markets and Distribution Channels
Choosing the right export markets and distribution channels helps businesses reach customers efficiently and strengthen their international brand presence.
3.3.1. Identifying Suitable Export Markets
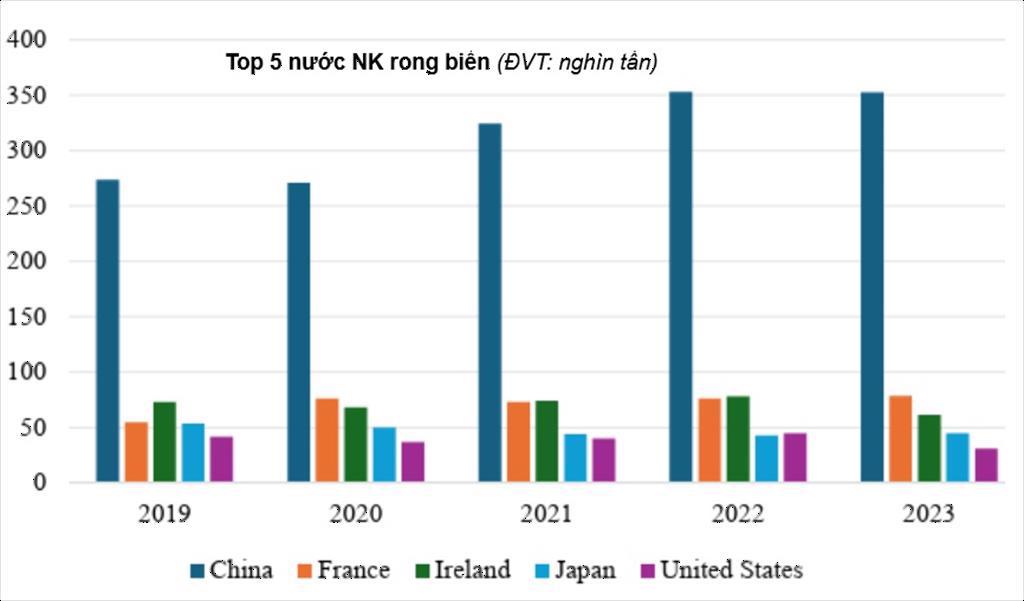
Top 5 Seaweed Importing Countries (Source: VASEP)
Currently, the five largest seaweed importers are China, France, Ireland, Japan, and the U.S. Other potential markets include South Korea, Canada, and EU countries where demand for healthy foods is rising. Market selection should prioritize countries with stable demand, strong purchasing power, and compatible quality standards.
3.3.2. Choosing Distribution Channels
Businesses can sell through traditional channels or e-commerce platforms. E-commerce allows direct access to global customers, reducing dependency on intermediaries and enabling rapid market testing. Particularly, exporting via Amazon offers significant advantages:
- Access to global customers
- Increased brand visibility across multiple markets
- Convenient order, payment, and logistics management with Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA)
- Easy access to consumer feedback for timely product adjustments
3.4. Logistics and Transportation
To export seaweed efficiently, businesses must ensure fast, safe shipping while maintaining product quality for international customers.
3.4.1. Choosing Appropriate Transportation Methods
Businesses can choose between sea freight and air freight:
- Sea freight: lower cost, suitable for large shipments; requires sealed, moisture-proof packaging and cold-chain if transporting fresh seaweed.
- Air freight: fast, suitable for small or perishable shipments needing immediate delivery.
Each method has its own advantages, so businesses should flexibly combine them according to demand and market conditions.
3.4.2. Monitoring the Transportation Process
To ensure products arrive safely and on time, businesses must proactively manage and monitor the entire shipping process—including route tracking and cargo condition checks. This minimizes risks of damage or loss, maintains product quality, and enhances brand reputation internationally.
3.5. Marketing and Brand Building in the International Market
To strengthen competitiveness and create market presence, businesses must deploy a comprehensive marketing strategy, combining online promotion with trade promotion activities. Online, businesses should leverage e-commerce platforms and global social networks to showcase products, interact with customers, and collect feedback.

At the same time, participating in international fairs and exhibitions helps build credibility, connect with partners, and expand distribution networks. Packaging and brand messaging should highlight Vietnamese origin, nutritional value, and quality commitment to build trust and clear recognition.
Read more: Brand Building — A Key Success Factor for Businesses
4. Important Considerations When Exporting Vietnamese Seaweed
In the process of expanding Vietnamese seaweed into global markets, aside from key competitive factors, the following considerations help minimize risks, enhance product value, and build a trustworthy international image.
4.1. Invest in Product Development and Value Addition
To stay competitive in global markets, businesses must continuously improve products and diversify processing methods. This helps upgrade product quality, optimize production processes, and meet international standards. Value-added product development also increases profit margins and differentiates businesses from competitors.
4.2. Build a Sustainable and Trustworthy Vietnamese Brand
To create a strong presence internationally, businesses need to build a brand associated with transparency, safety, and sustainability. This includes clear traceability, environmentally friendly farming practices, and eco-friendly packaging.
When businesses share a consistent brand story—from farming areas to finished products—Vietnamese seaweed will gain trust and increase its value in the eyes of global consumers.
5. Conclusion
Vietnamese seaweed is facing significant opportunities to expand exports thanks to abundant supply and rising global demand. With the right investment in quality, standards, and market strategy, Vietnamese seaweed can fully compete in many international markets.
If your business needs support with export procedures, documentation, international certifications, or selling on global e-commerce platforms like Amazon, AGlobal is ready to accompany you!
AGlobal — the best cross-border e-commerce solution for businesses.
Register for free 1-on-1 consultation tailored to your industry here!
