
Overview of GMP standards for businesses
In the context of modern manufacturing, GMP plays an increasingly crucial role in helping businesses control quality and ensure the safety of the final product.
This article provides an overview of GMP, the GMP certification process, and the specific requirements for applying GMP in food production.
1. What is the GMP Standard?
Before delving into more detailed content, let’s first explore what GMP actually is.
1.1. Definition of GMP
GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) is an international set of standards that outlines the essential principles and guidelines required to control all factors that may affect product formation, ensuring that the final output is consistently high-quality and safe for consumers.
In Vietnam, GMP is mandatory for facilities involved in the manufacturing, processing, and packaging of product groups that require strict hygiene conditions, such as food, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and medical devices.
See more: What is GMP? GMP requirements and the implementation process of Good Manufacturing Practices
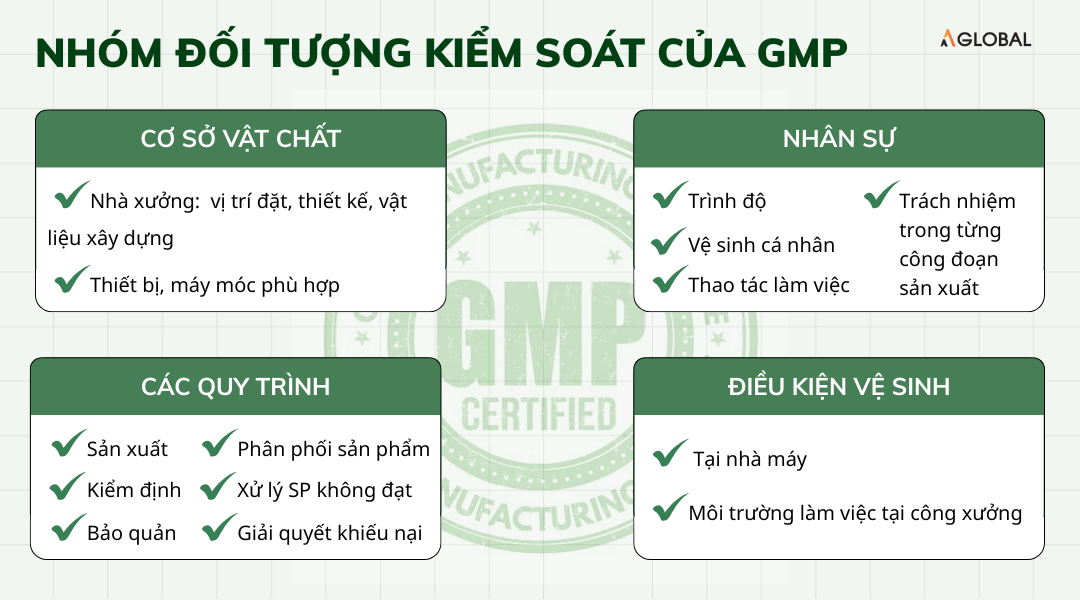
1.2. Scope and Control Subjects of GMP
The scope and control subjects of GMP are broad and may vary by industry. However, GMP basically focuses on controlling the following key factors:
Facilities
- Factory: location, design, and construction materials.
- Equipment and machinery suitable for producing high-quality products.
Personnel
Qualifications, work practices, personal hygiene requirements, and responsibilities of employees in each production step.
Processes
- Production processes.
- Quality control processes for products, raw materials, work procedures, and hygiene.
- Processing, storage, and product distribution procedures.
- Procedures for handling non-conforming products.
- Procedures for resolving customer complaints.
Sanitation Conditions
At the factory and working environment at the facility.
1.3. Common GMP Standards Today
There are three popular GMP standards currently applied:
EU GMP (European Union – Good Manufacturing Practice)
EU GMP is the European GMP standard, issued by the European Medicines Agency (EMA), mainly applied to pharmaceuticals and dietary supplements exported to the EU market.
Today, EU GMP is one of the highest-level quality standards and is difficult to obtain. Facilities certified with EU GMP are widely recognized in many demanding markets thanks to their high product quality and transparent production processes.
GMP WHO
This is a system of standards ensuring that products are manufactured and controlled consistently according to the quality standards issued by the World Health Organization (WHO).
GMP WHO is often applied in the production of medicines, vaccines, and pharmaceuticals in international markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, thanks to its flexibility and accessibility compared to EU GMP.
cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices)
cGMP is the GMP standard issued by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), emphasizing the principle of “current”: manufacturing facilities must use updated technologies, equipment, and procedures to comply with regulations.
cGMP is typically applied to products exported to the U.S. and other markets with similar requirements, helping businesses maintain consistent product quality and enhance international credibility.
2. GMP Certification
Below is essential information businesses should know about GMP certification.
2.1. What is GMP Certification?
GMP certification is an official document confirming that a manufacturing facility has fully complied with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). In other words, GMP certification verifies that the company has met all GMP regulations, including production processes, quality control, and product storage.
Having GMP certification not only helps businesses ensure safe and high-quality output products but also increases credibility, facilitates export to international markets, and meets the legal requirements of many countries.
2.2. Steps to Achieve GMP Certification
To obtain GMP certification, a business must implement a structured process including the following steps:
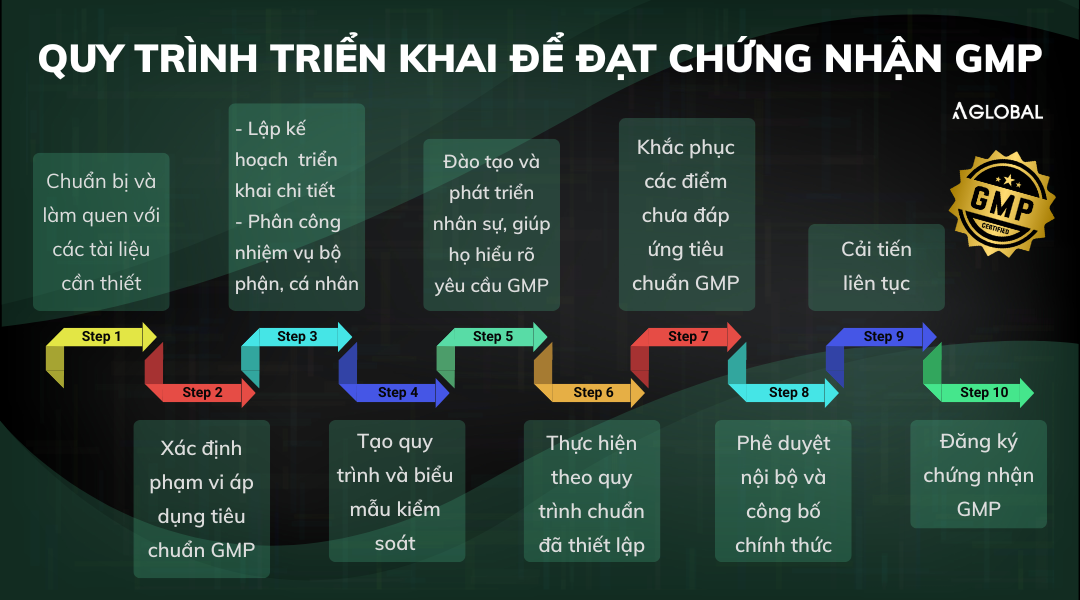
Step 1: Preparation and familiarization with required documents
- Current legal regulations applicable to the industry and product.
- GMP standards relevant to the product being manufactured.
- Technical requirements for operation and quality control.
- Feedback from customers and stakeholders.
- Results from product research and sample testing.
The goal of this step is to ensure the business thoroughly understands the mandatory requirements and necessary conditions to implement GMP effectively.
Step 2: Identify the scope of GMP application
The business must define which departments, processes, and products will be controlled under GMP, from production and processing to packaging and distribution.
Step 3: Planning and task assignment
Develop a detailed implementation plan, including timelines and assigning responsibilities to departments and individuals involved in the GMP process.
Step 4: Establish procedures and control forms
Set up Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), control forms, and work instructions for each stage of production to ensure all activities comply with GMP requirements.
Step 5: Personnel development
Train and enhance employee competencies to ensure they understand GMP requirements and follow the correct production procedures.
Step 6: Implement the established procedures
The business operates, manufactures, and controls processes according to the defined SOPs and control forms to ensure compliance with GMP.
Step 7: Handle non-compliance and outstanding issues
Before submitting the evaluation dossier, the business must review and resolve all outstanding issues, correcting any deviations from GMP standards.
Step 8: Internal approval and official announcement
All GMP systems and procedures are internally approved and prepared for official evaluation by competent certification bodies.
Step 9: Internal audit and continuous improvement
Conduct internal audits to detect areas needing improvement, thereby enhancing system effectiveness and preparing for certification evaluations.
Step 10: Submit GMP certification application
Finally, the business submits the GMP certification dossier to the regulatory authority or conformity assessment organization to complete the certification process.
2.3. Dossier for Initial Certification and Recertification Evaluation
A business submits an application for initial GMP certification when registering for the first time. If the business already has certification, it must apply for GMP recertification to maintain validity.
Dossier for initial GMP certification
Businesses must prepare the following documents:
- Application for GMP certification.
- Legal documents of the business: Business registration license, Enterprise registration certificate, Environmental impact assessment report, and relevant permits.
- Quality management system documents: Organizational chart; Production and quality control procedures; List of equipment and machinery; Maintenance and calibration procedures.
- Facility condition documents: Factory layout; Water supply, wastewater treatment system, water quality inspection results; Environmental control systems; Sanitation and occupational safety documentation.

Dossier for GMP recertification
GMP certification is valid for 3 years from the date of issuance. Six months before expiration, businesses must submit a recertification dossier. The dossier includes:
- Application for recertification: Report on production activities and GMP compliance.
- Production activity reports: GMP maintenance measures; Product quality inspection reports; Internal audit results; Corrections of deviations (if any).
- Updated facility documents: Changes in production processes, equipment, or personnel (if any); New environmental and safety assessments; Latest quality testing certificates.
See more: Dossier for initial and renewal GMP certification evaluation
3. GMP Standards in Food Production
Applying GMP in food production is increasingly essential to ensure product safety and quality.
3.1. Why GMP is Needed in Food Production
GMP is crucial because it is an effective tool for ensuring food safety proactively.
Through strict regulations and controls over all factors affecting quality — from raw materials, equipment, and production environment to employee practices — GMP helps prevent biological, chemical, and physical contamination from input to processing.
Standardized procedures and clear documentation ensure consistent quality across production batches and support traceability when necessary.
GMP also helps businesses comply with regulations, reduce operational risks, minimize losses from defective or recalled products, and enhance reputation and competitiveness in the food market.
3.2. GMP Standards in Food Production
GMP applies to various food supply chain segments, especially facilities directly involved in food processing and handling, such as:
- Food manufacturing and processing companies
- Producers of food additives, ingredients, and food-contact packaging
- Food packaging, storage, and distribution companies
- Restaurants and canteens (when operating on a large scale under relevant standards)

Specific requirements include:
- Environmental control: clean factories, proper layout, pest control, and control of temperature, humidity, and water quality.
- Raw material management: clear origin, hygiene standards, proper storage, and inspection before use.
- Process control: standardized procedures for each step to ensure compliance and minimize contamination.
- Equipment control: maintenance, cleaning, and calibration of equipment in contact with food.
- Personnel control: training, hygiene practices, protective clothing, health checks, and clear responsibility assignment.
- Product quality control: testing raw materials, semi-finished and finished products before release.
- Documentation management: complete records for production, quality checks, storage, and distribution to support traceability.
- Handling non-conforming products: separation, recall, and root-cause investigation.
- Sanitation and disinfection: regular cleaning of equipment, surfaces, and factory areas.
- Continuous improvement: regular system evaluations and improvements.
See more: Detailed procedures for issuing Certificates of Origin (CO) 2025
4. Conclusion
As consumers increasingly prioritize food quality and safety, applying GMP standards in production becomes essential for businesses to ensure safe, consistent products and enhance market credibility.
AGlobal – the best cross-border e-commerce solution for businesses.
Register for a free one-on-one consultation tailored to your industry here!
