
Halal Standards & International Growth Opportunities for Businesses
In the context where the Muslim consumer group accounts for nearly 25% of the global market size, the Halal standard plays an extremely important role for businesses. It not only protects consumer safety and rights but also helps enterprises enhance credibility and expand business effectively.
1. What is the Halal standard?
The Halal standard is not only a religious requirement but also a system that determines whether a product is permissible according to Islamic law. Understanding Halal helps both businesses and consumers identify products that comply with religious regulations, thereby ensuring trust and protecting user rights.
1.1. The concept of “Halal Standard” under Sharia law
From the perspective of Sharia law, Halal means “permissible” or “allowed,” while its opposite, Haram, means “forbidden.” Therefore, the Halal standard is a system of regulations used to determine whether a product or production process is permitted according to Islamic law.
Although this concept is often associated with food, in reality, the Halal standard covers various fields such as beverages, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, services, and even factory operation procedures.
1.2. Purpose of the Halal standard
The most important goal of the Halal standard is to protect the health and rights of Muslim consumers. Through a clear set of regulations, Halal ensures that products do not contain prohibited ingredients and are produced in clean, safe, and transparent conditions.
Beyond its religious meaning, the Halal standard also helps businesses improve management quality and build trust with global customers. Meeting this standard opens significant opportunities for businesses to enter the Muslim market — which accounts for 25% of the global population today.
2. What is Halal food?
2.1. Characteristics of Halal food
Halal food refers to products that meet religious requirements and are permissible under Sharia law. Each Muslim-majority country has its own Halal certification body (Halal Examination Agency) responsible for inspecting, supervising, and issuing Halal certificates before products enter the market.
In Vietnam, consumers can identify Halal food through:
- Halal labels on products: Meat, beverages, instant noodles, or processed foods must display a logo or certification from reputable Halal organizations.
 Products are labeled Halal
Products are labeled Halal
- Halal-certified facilities: Some factories specialize in Halal production, ensuring ingredients and processes comply with regulations.
- Halal restaurants: Indian, Malaysian, or other Muslim-country restaurants often serve Halal dishes; users may check online or ask local Muslim communities.
- Supermarkets: Some major supermarkets in Vietnam offer Halal foods such as meat, rice, and canned products.
Consumers should always check the label and product origin to ensure Halal compliance, especially for traditional dishes or items without direct certification.
2.2. Requirements for ingredients and production processes
Ingredients used in Halal food must be natural and free from Haram substances. Common Halal-friendly ingredients include:
- Meat from animals slaughtered according to Islamic rites: beef, lamb, goat, chicken, bird species, duck…
- Fish, honey, milk from cows, sheep, goats, or camels.
- Fresh vegetables, fruits, nuts (peanuts, cashews, hazelnuts) and grains (wheat, rice, oats…).
The slaughtering and processing procedure must also follow strict rules:
- The slaughterer must recite the name of Allah before slaughtering.
- Tools must be sharp to ensure humane treatment.
- Animals must be alive and healthy before slaughter, and all blood must be drained.
- Only Muslims or Jews may perform the slaughter.
- Animals must be naturally raised and not fed animal by-products.
These regulations ensure that Halal food is both religiously compliant and safe and transparent for consumers.
Read more: What are consumer goods? Main product groups and 2025 trends
3. Role and significance of the Halal certificate
The Halal certificate plays a key role in confirming that products, foods, or services comply with Islamic regulations. This is not only a legal basis but also helps businesses build customer trust and expand opportunities in Muslim-majority markets.
3.1. What is a Halal certificate?
A Halal certificate is a document verifying that a product or manufacturing facility meets all Halal standards according to Sharia law. It proves that ingredients, production processes, and all related factors are “permissible” and safe for Muslim consumers.

Sample Halal certificate issued by GHC
In addition, the certificate allows businesses to place the Halal mark on their products, confirming that the product meets Halal Food standards.
Read more: Detailed procedure for obtaining a Certificate of Origin in 2025
3.2. Benefits of the Halal certificate for businesses and consumers
Having a Halal certificate brings practical benefits for both businesses and consumers.
For businesses, a Halal certificate helps affirm credibility, enhance product quality, and expand business opportunities in Muslim markets. Specifically:
- Easily gain the trust of Muslim customers — a group accounting for 25% of the global population.
- Improve brand credibility, reputation, and product quality through compliance with Halal standards.
- Expand cooperation opportunities with partners requiring Halal certification.
- Increase export potential to Muslim markets and countries with large Muslim communities.
- Boost revenue and profit through market expansion.
For consumers, the Halal certificate provides safety and peace of mind:
- Compliance with Islamic law and assurance that products are safe and permissible.
- Clear understanding of raw materials and production processes, minimizing risks associated with unsafe products.
- Protect personal and family health.
- Enable informed decisions by choosing reputable, trustworthy products.
It is clear that the Halal certificate not only helps businesses enhance their reputation and expand markets but also provides consumers with safety and confidence in their everyday purchasing decisions.
Read more: Product development strategy — 7 phases that determine success
4. Halal certification process for businesses
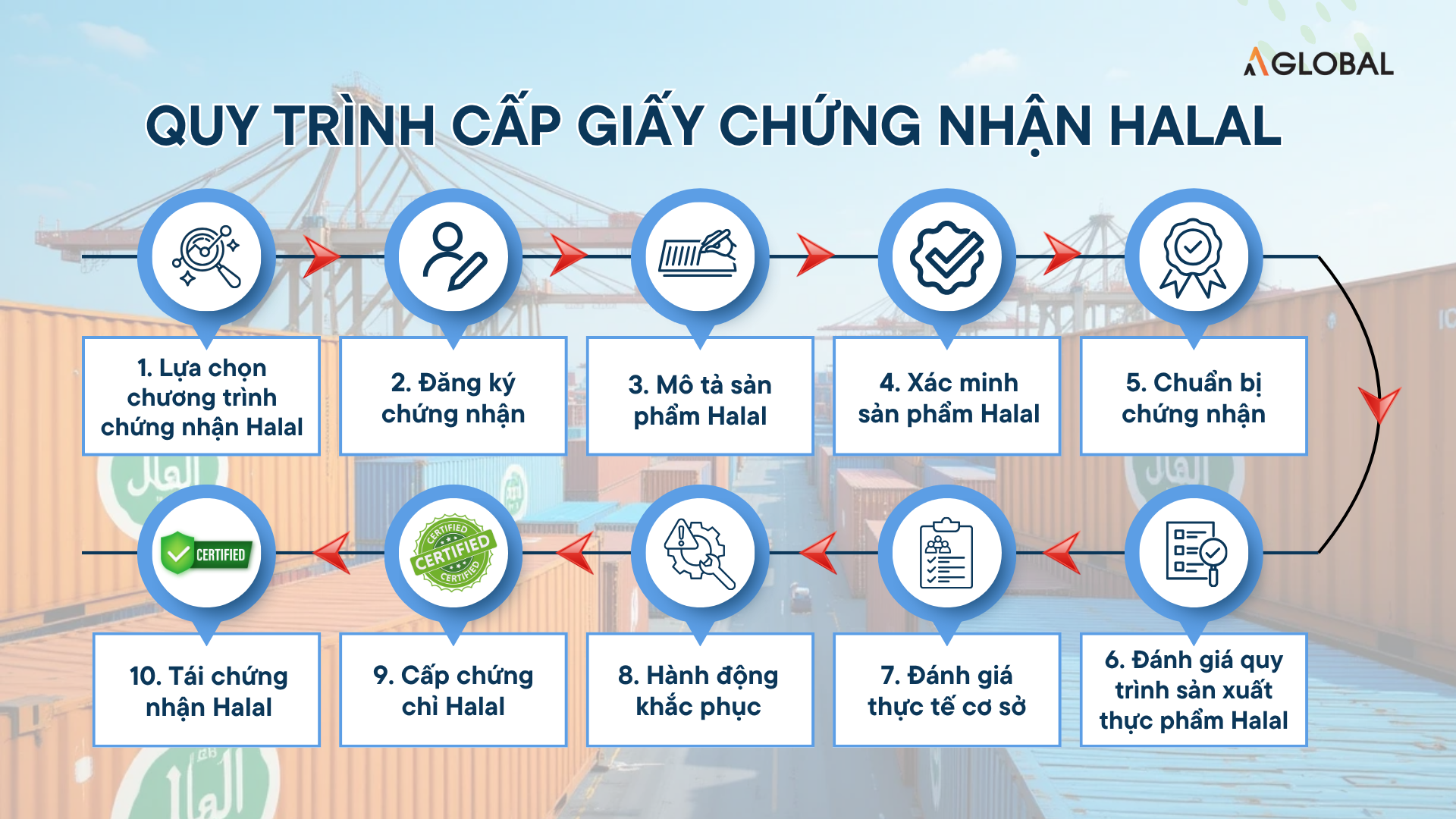
10-step Halal certification process diagram
To obtain Halal certification, businesses must follow a strict, standardized process consisting of multiple steps to ensure that all ingredients, production processes, and facilities fully comply with Halal standards:
Step 1: Choose a suitable certification program
Businesses need to research and select the Halal program that fits their export markets. They may register for one or multiple programs to support international trade. Currently, three popular certification programs include:
- JAKIM – Malaysia’s Halal authority, known for strict assessment and broad international recognition.
- MUI – Indonesia’s Halal body, required for exporting to Indonesia, with strong emphasis on raw material control.
- GCC Halal – certification program for Gulf countries, applying stringent standards regarding slaughtering, hygiene, and traceability.
Step 2: Register for certification
Businesses must prepare and submit the following documents:
- Business registration license
- Company profile (including organizational chart)
- Operation license
- Production flowcharts for certified products
- Laboratory test results for certified products
- Other certificates such as ISO, HACCP, GMP, GAP (if any)
After submitting all documents, enterprises proceed to register for the Halal certification with the relevant organization.
Step 3: Describe the product
Provide detailed lists of ingredients, components, and production processes for evaluation.
Step 4: Product verification
The certification body checks whether the product complies with Halal standards and provides feedback.
Step 5: Prepare for assessment
Enterprises sign the assessment contract and prepare documents and facilities for the official inspection.
Step 6: Document and process assessment
The certification body reviews documents, production processes, and Halal assurance measures.
Step 7: On-site inspection
Inspectors examine facilities, workshops, interview staff, and assess production activities.
Step 8: Corrective actions
If any non-compliance is found, businesses must implement corrective measures and report back.
Step 9: Issuance of Halal certificate
Once all requirements are met, the Halal certificate will be issued, usually valid for one year.
Step 10: Recertification
When the certificate expires, businesses must repeat the evaluation process to renew it.
5. Notes when using the Halal certificate
Once the Halal certificate is obtained, businesses must maintain full compliance throughout production and use the Halal mark correctly according to regulations.
5.1. Regulations for using the Halal mark on products

Common Halal certification labels
The Halal mark is important proof that a product complies with Islamic requirements. Therefore, businesses must follow regulations to ensure transparency and avoid misleading consumers. Key principles include:
- Only attach the Halal mark to certified products still under validity.
- Keep the original design; it may be resized proportionally or recolored, but must remain clear and readable.
- Do not modify, add, or remove details, or use the Halal mark as the certifier’s emblem.
- The Halal mark must be accompanied by the name or logo of the certified enterprise.
- Do not use the mark in ways that can mislead customers about the certification scope.
5.2. Validity period and legal compliance of the certificate
Each Halal certificate has a specific validity period, generally ranging from 1–3 years depending on the certification program.
To maintain validity, businesses must continuously comply with Halal standards throughout the certificate’s lifespan:
- Production processes must remain consistent with the original Halal requirements.
- If violations occur (Haram ingredients, poor hygiene, etc.), the certificate may be revoked immediately.
- Certification bodies may conduct periodic or surprise inspections.
Businesses must also renew their certification before expiration to avoid having to reapply from the beginning.
6. Conclusion
The Halal standard is not only a religious requirement but also an essential measure of product quality, safety, and transparency in Muslim markets. By following the certification process and maintaining compliance throughout production, businesses can strengthen their reputation, gain competitive advantages, and build strong trust with customers.
AGlobal – the best cross-border e-commerce solution for businesses.
Register for a free 1-on-1 consultation tailored to your industry here!
