
What is Prime Rate? What you need to know
In business, interest rates have always been a key factor determining the cost of capital and profit margins. Among them, the Prime Rate is a crucial concept that banks use as a basis for calculating other types of interest rates. Understanding what the Prime Rate is helps businesses anticipate market trends and make more effective financial decisions.
1. What is the Prime Rate?
The Prime Rate refers to the base interest rate – the most favourable rate that commercial banks offer to large, reputable corporate clients with low credit risk. Because this group of clients poses almost no risk of default, they are entitled to significantly lower interest rates compared to individuals or smaller enterprises.

A distinctive feature of the Prime Rate is that it is not a fixed or uniform number. Each bank may publish its own rate, but the financial market typically uses the average rate from the largest banks as a benchmark reference.
For instance, in the United States, the Prime Rate is calculated by adding a certain percentage (X%) to the Federal Reserve’s benchmark rate (Fed Funds Rate). This means that if the Fed Funds Rate is currently 5%, the Prime Rate would be 5% + X%. This calculation provides banks with a clear reference point for pricing various loans.
2. How does the Prime Rate work?
The Prime Rate is considered the benchmark for the entire credit system. Most other interest rates – such as for mortgages, car loans, and credit cards – are determined based on the Prime Rate. Once you understand what the Prime Rate is, you can better grasp how interest rates directly impact your finances.
Example: A credit card might specify an interest rate of Prime Rate + 5%. This means that when the Prime Rate increases, the card’s interest rate rises accordingly, maintaining a constant margin of 5%. This mechanism allows banks to balance profitability while reflecting fluctuations in market funding costs.
According to data from the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (FRED), as of September 2025, the U.S. Prime Rate stood at 7.25%. Although this marks a slight decrease from the previous period (7.5%), it remains relatively high. This exerts significant pressure on small businesses, as borrowing costs rise, while large corporations are less affected thanks to their stronger credit profiles.
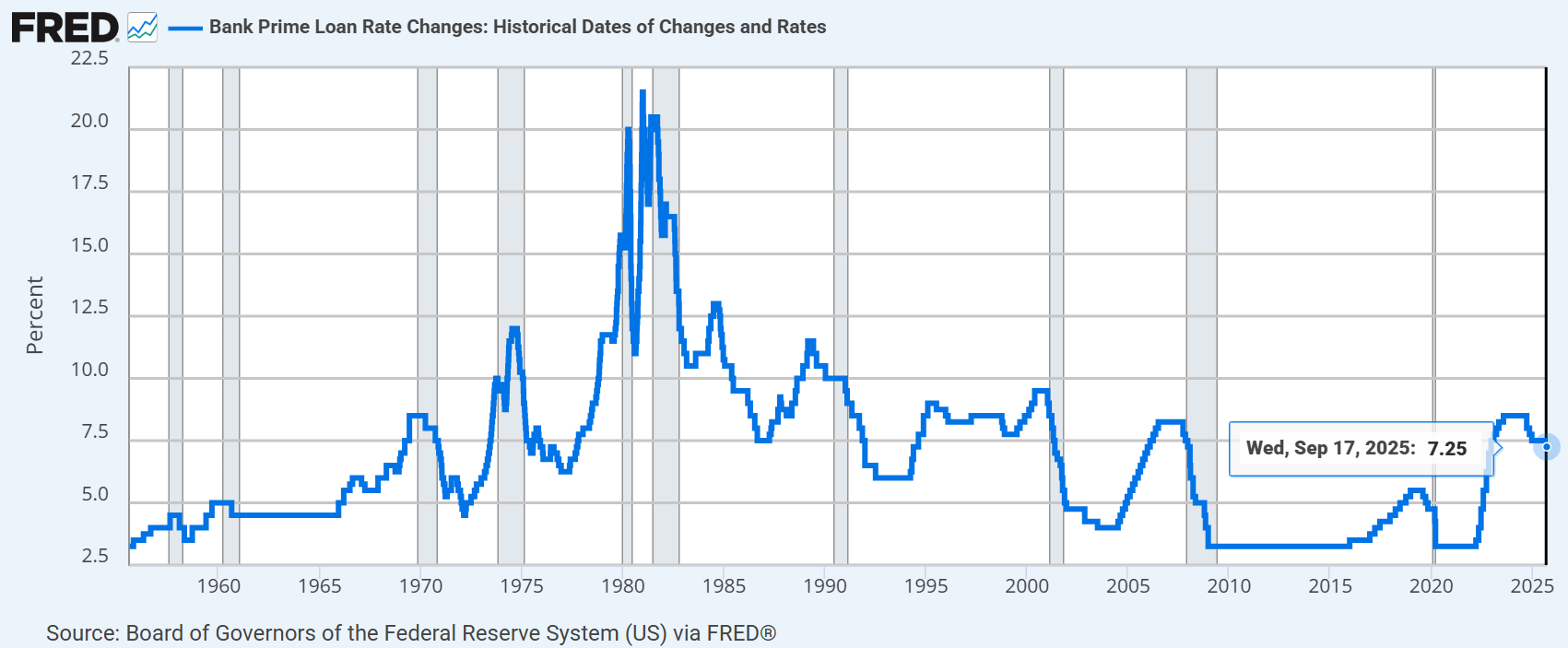
Historical Prime Rate in the U.S., September 2025: 7.25%. (Source: FRED)
The base interest rate is also a tool used by governments to regulate monetary policy, aiming to stabilise prices, stimulate growth, and guide lending activity.
3. How is the Prime Rate determined?
To fully understand what the Prime Rate is, we must also understand how it is determined. The Prime Rate is influenced by various economic and financial factors, specifically:
- Policy interest rate: The central bank’s benchmark rate (e.g. the Fed Funds Rate in the U.S. or refinancing rate in Vietnam) forms the foundation for calculating the Prime Rate.
- Interbank lending rate: The overnight borrowing cost between banks also impacts the Prime Rate.
- Banks’ cost of capital: Including the cost of raising funds through deposits, bond issuance, and open market operations.
- Capital supply and demand fluctuations: When borrowing demand is high, the Prime Rate tends to rise to balance risk.
- Credit risk: In periods of market volatility or increased default risk, banks may raise the Prime Rate to compensate.
In 2025, as inflation remains unstable in many countries, the Prime Rate has become a crucial tool for banks to adjust funding costs and alleviate credit pressure.
4. What is the impact of the Prime Rate?
The Prime Rate has a far-reaching influence on individuals, businesses, and the overall economy:
- For businesses: When the Prime Rate rises, borrowing costs increase, making it harder for companies – especially small and medium-sized enterprises – to expand production.
- For consumers: Interest rates on mortgages, car loans, and credit cards all increase in line with the Prime Rate, reducing spending capacity.
- For financial markets: The Prime Rate affects stock prices, bond yields, and investment flows. When it is high, capital often shifts towards savings rather than riskier investments.
- For macroeconomic policy: Governments or central banks use the Prime Rate as a regulatory tool to control inflation, stabilise prices, and direct credit activities.
Currently, with the Prime Rate in the U.S. and many major economies remaining elevated, e-commerce companies like Amazon are also affected. Consumers tend to cut spending, while funding costs for logistics and warehousing rise — forcing businesses to optimise expenses further.
Therefore, understanding what the Prime Rate is also means understanding one of the key instruments of economic regulation.
5. How has the Prime Rate changed over time?
The base interest rate set by the State Bank of Vietnam has undergone multiple adjustments depending on economic and financial market conditions.
The chart below illustrates key milestones in the changes to the base interest rate from 2000 to the present:
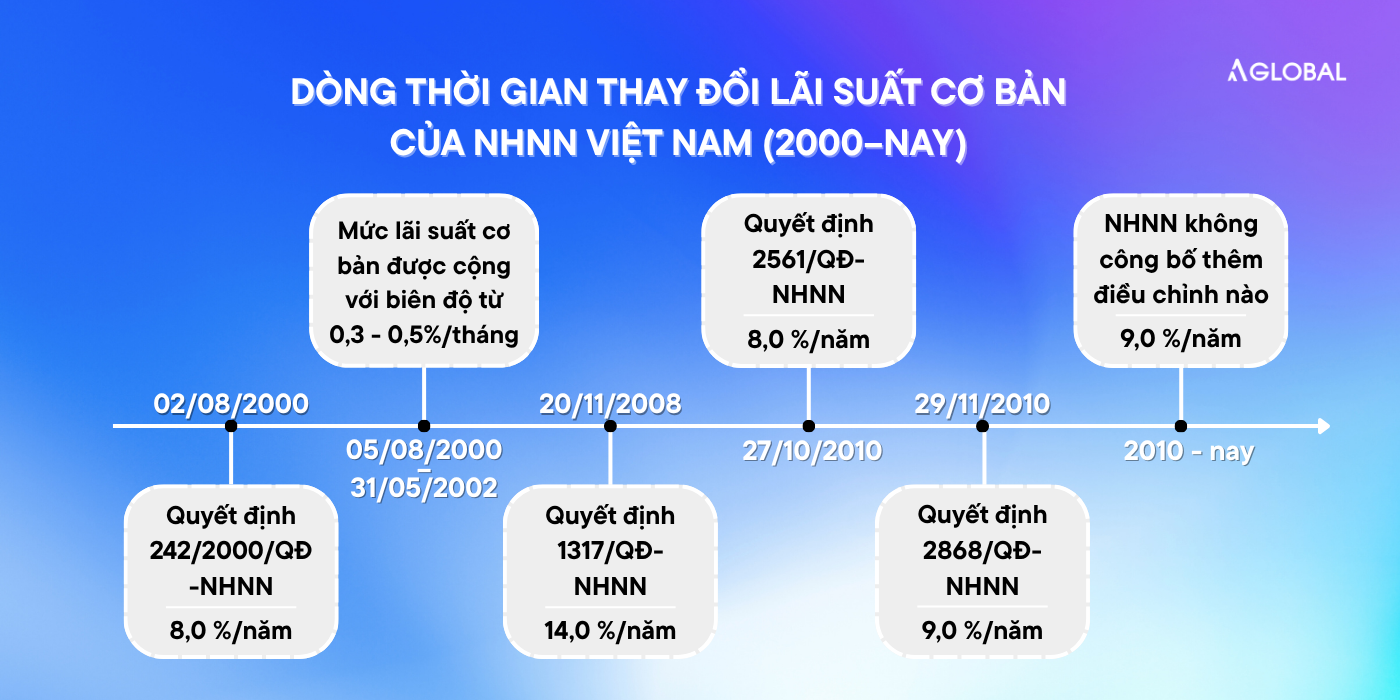
Timeline of changes in the State Bank of Vietnam’s base interest rate (2000–present)
Monitoring the Prime Rate is important not only for businesses but also for consumers, as it reflects the overall “health” of the economy and helps forecast capital cost trends in the near future.
6. What remains unaffected by changes in the Prime Rate?
Loans or credit lines with fixed interest rates are not affected by fluctuations in the Prime Rate. These typically include student loans, fixed-rate mortgages, or pre-agreed savings packages.
In other words, even if the Prime Rate rises or falls over time, borrowers or depositors under fixed-rate contracts continue to enjoy the originally agreed rate. This is the key advantage of fixed interest rates — allowing customers to better plan long-term finances and avoid risks from market volatility.
Learn more: Discover how to earn billions selling on Amazon with just 5 simple steps.
7. Conclusion
Understanding what the Prime Rate is not only helps businesses forecast interest rate trends but also optimise their long-term financial strategies. Therefore, mastering fundamental financial indicators such as the Prime Rate enables greater control over cost management, investment, and international business expansion.
AGlobal – the best cross-border e-commerce solution for businesses.
Register for a free 1-on-1 consultation tailored to your industry Here!
